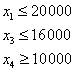![]() … number
of units of product A to be produced
… number
of units of product A to be produced
![]() … number
of units of product B to be produced
… number
of units of product B to be produced
![]() … number
of units of product C to be produced
… number
of units of product C to be produced
![]() … number
of units of product D to be produced
… number
of units of product D to be produced
P … total profit
2. Objective
function
Maximise: ![]()
The first set of constrains is related to the limited sources. There are requirements of the production in the left-hand side and maximal disposable capacity (or financial funds) in the right-hand side.
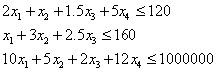
Following constrains reflect the fact that the production can have upper or lower limits usually given by contracts with customers.